April 3, 2020 by John Fernandez
For African-Americans, Especially, Focus on Heart Health Should be Year-Round

There’s always something happening in February, particularly in South Florida, but for the region’s African-American population, two events in particular – Black History Month and American Heart Month – have extra importance.
Why? Because nationwide, African-Americans are far more likely to be diagnosed with and die from coronary heart disease.
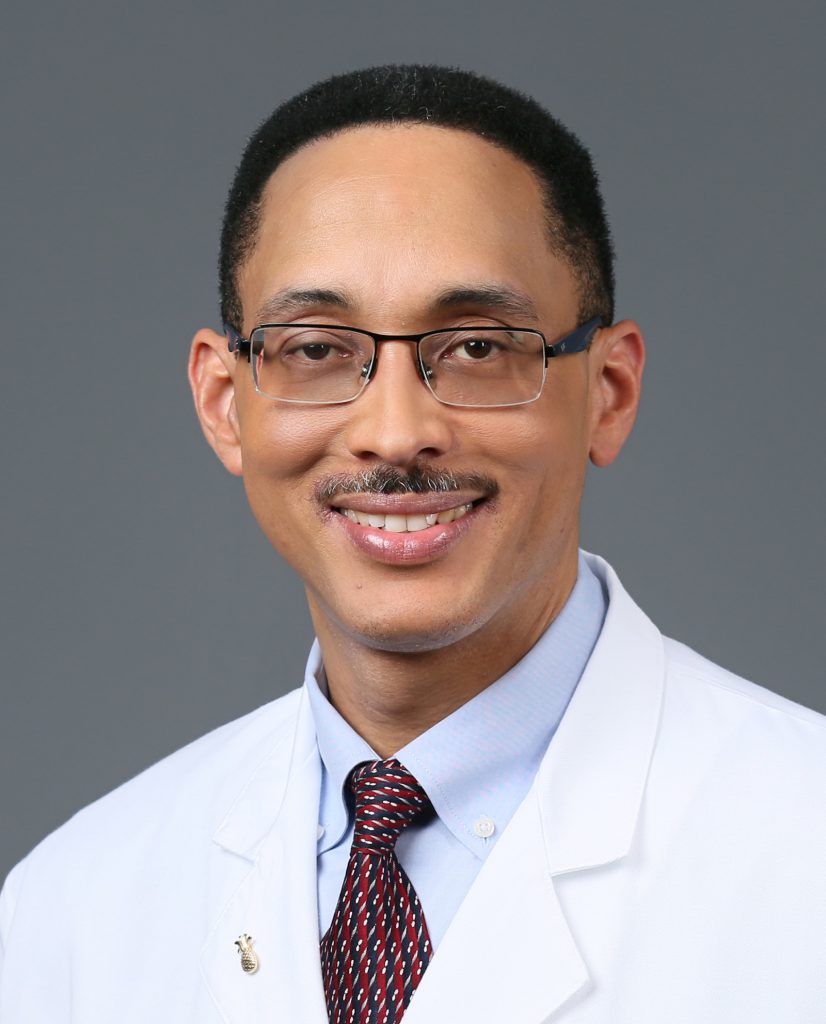

“In terms of cardiovascular health, there is a disproportionate occurrence of risk factors in African-Americans,” says Marcus St. John, M.D., interventional cardiologist with Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute, part of Baptist Health South Florida.
According to statistics from the American Heart Association, heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States. Every year, one in four deaths is caused by heart disease – more than all forms of cancer combined. One particular group, however, has a much higher risk of heart disease.
Statistics from BlackDoctor.org show that African-Americans are:
• 40 percent more likely to have hypertension (high blood pressure), yet 10 percent less likely than their non-Hispanic, White counterparts to have it under control
• More than three times as likely to die from heart disease caused by high blood pressure than Caucasians
• More likely to die from stress-related heart attacks (African-American men) than any other ethnic group in the U.S.
There could be a variety of reasons for these disparities, according to Dr. St. John, who also serves as Medical Director of the Cardiac Catheterization Lab at Baptist Hospital.
“Some of it may be due to genetic predispositions. For instance, we know that African-Americans are more likely than other groups to be salt-sensitive, making them more likely to develop hypertension, a major contributor to coronary artery disease,” Dr. St. John says.
Socio-economic conditions, healthcare illiteracy and lack of access are also factors, he says, as is a culturally rooted distrust of institutionalized healthcare.
“As a result, by the time they do eventually get diagnosed, their heart disease may have progressed further and be far more serious, which contributes to a higher death rate for this particular population, ” Dr. St. John says.
The good news, however, is that heart disease can often be prevented by making healthy choices and managing your health conditions.

First, he says, know your numbers. “Knowing your blood pressure and cholesterol numbers – what they are and where they should be – is important and can easily be done at your local pharmacy or a walk-in clinic.”
Beyond that, making healthy choices is key to maintaining a healthy heart, Dr. St. John says. “In most cases, heart disease can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle.”
Heart-healthy lifestyle choices, according to Dr. St. John, include:
• Not smoking
• Maintaining a healthy weight
• Controlling blood sugar and cholesterol
• Limiting foods high in salt, sugar and fat
• Increasing consumption of fruits and vegetables
• Treating high blood pressure
• Getting adequate sleep (7 to 8 hours a night, minimum)
• Exercising regularly – at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity a week
• Getting regular check-ups
“First thing I advise is to take a 15-minute walk, whether you’re at work or at home,” Dr. St. John says. “That’s an easy starting point. And if you’re used to walking, make it a 30-minute walk. Then, start focusing on other ways you can maintain a healthy heart.”
Cardiologists have the training, tools and technology and to help treat your heart disease, Dr. St. John says. “But it’s up to you to make smart choices and take care of your heart – not just in February but all year long.”

top stories










There are no comments